- Vpn Site To Site
- Cisco Vpn Site To Site
- Asa Vpn Load Balancing Site To Siteground
- Asa Vpn Load Balancing Site To Site Free
VPN load balancing is a mechanism that is used in order to equitably distribute network traffic among the devices in a virtual cluster. Load balancing is based on simple distribution; it does not take in to account throughput utilization or other factors. If asa doens't support site-to-site vpn loadbalancing by design, im looking to leverage some scripting but initially i need to have a passwordless login to asa using key-based or certificate authentication / login. #Look #Save Shop for Best Price Windows Server Auto Connect Vpn And Asa Vpn Load Balancing Site To Site.
Contents
Introduction
Load balancing is the ability to have Cisco VPN Clients shared across multiple Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) units without user intervention. Load-balancing ensures that the public IP address is highly available to users. For example, if the Cisco ASA that services the public IP address fails, another ASA in the cluster assumes the public IP address.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
You have assigned IP addresses on your ASAs and configured the default gateway.
IPsec is configured on the ASAs for the VPN Client users.
VPN users are able to connect to all ASAs with the use of their individually assigned public IP address.
Eligible Clients
Load balancing is effective only on remote sessions initiated with these clients:
Cisco VPN Client (release 3.0 or later)
Cisco VPN 3002 Hardware Client (release 3.5 or later)
CiscoASA 5505 when acting as an Easy VPN client
All other clients, including LAN-to-LAN connections, can connect to a security appliance on which load balancing is enabled, but they cannot participate in load balancing.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
VPN Client Software Releases 4.6 and later
Cisco ASA Software Releases 7.0.1 and later
Note: Extends load balancing support to ASA 5510 and ASA models later than 5520 that have a Security Plus license with the 8.0(2) version.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
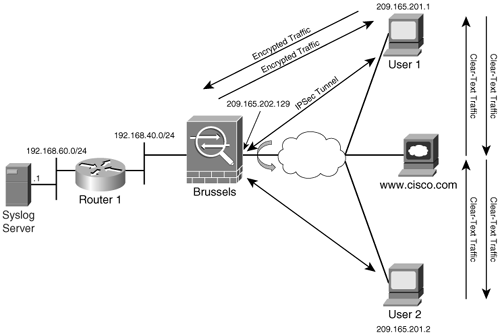
Network Diagram
Vpn Site To Site
This document uses this network setup:
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Restrictions
Cisco Vpn Site To Site
VPN virtual cluster IP address, User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port, and shared secret must be identical on every device in the virtual cluster.
All devices in the virtual cluster must be on the same outside and inside IP subnets.
Configuration
IP Address Assignment
Ensure that the IP addresses are configured on the outside and inside interfaces and you are able to get to the Internet from your ASA.
Note: Ensure that ISAKMP is enabled on both the inside and outside interface. Select Configuration > Features > VPN > IKE > Global Parameters in order to verify this.
Cluster Configuration
This procedure shows how to use the Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) to configure load balancing.
Note: Many of the parameters in this example have default values.
Select Configuration > Features > VPN > Load Balancing, and check Participate in Load Balancing Cluster to enable VPN load balancing.
Complete these steps to configure the parameters for all ASAs participating in the cluster in the VPN Cluster Configuration group box:
Type the IP address of the cluster in the Cluster IP Address text box.
Click Enable IPSec Encryption.
Type the encryption key in the IPSec Shared Secret text box and type it again in the Verify Secret text box.
Configure the options in the VPN Server Configuration group box:
Select an interface that accepts the incoming VPN connections in the Public list.
Select an interface that is the private interface in the Private list.
(Optional) Change the priority that the ASA has in the cluster in the Priority text box.
Type an IP address for the Network Address Translation (NAT) Assigned IP Address if this device is behind a firewall that uses NAT.
Repeat the steps on all the participating ASAs in the group.
The example in this section uses these CLI commands to configure load balancing:
Monitoring
Select Monitoring > Features > VPN > VPN Statistics > Cluster Loads to monitor the load balancing feature on the ASA.
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
show vpn load-balancing—Verifies the VPN load balancing feature.
Troubleshoot
Use this section to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
debug vpnlb 250—Used to troubleshoot the VPN load balancing feature.
Related Information
Introduction
This document describes the Director Election process in a VPN load-balancing scenario with the Cisco 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA).
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco ASA 5500-X that runs software Version 9.2.
Note: This document also applies to all software versions, since the feature was first introduced in Version 7.0(1).
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Asa Vpn Load Balancing Site To Siteground
Background Information
VPN load balancing is a mechanism that is used in order to equitably distribute network traffic among the devices in a virtual cluster. Load balancing is based on simple distribution; it does not take in to account throughput utilization or other factors. A load-balancing cluster consists of two or more devices, a director and one or more secondary devices, and these devices do not have to be configured identically.
Load-Balancing Algorithm
Here is an overview of the load-balancing algorithm:
- The director device maintains a sorted list of secondary cluster members in ascending order of inside IP addresses.
- The load is computed as an integer percentage (number of active/maximum sessions) that is supplied by each secondary cluster member.
- The director device redirects the IPSec/Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN tunnel to a device with the lowest load first, until it is one percent higher than the other devices.
- The director device redirects to itself only when all of the secondary cluster members are one percent higher than the director device.
Here is an example with one director and two secondary cluster members:
- All nodes begin with a zero-percent load, and all percentages are rounded to the nearest half-percent.
- The director device takes the connection if all of the members have a load that is one percent higher than the director device.
- If the director device does not take the connection, the session is taken by the backup device that currently has the smallest load percentage.
- If all of the members have the same load percentage, then the backup device with the least amount of sessions takes the session.
- If all of the members have the same load percentage and the same number of sessions, then the backup device with the least amount of IP addresses takes the session.
Director Election Process
The VPN load balancing Director Election process is performed on the cluster outside network. There are two types of data exchanged on the outside network:
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets for the cluster IP address that are used for director discovery are exchanged. The maximum number of ARP packets that are sent for the cluster IP address in order to discover the director is:
(10 - priority) + 1
Here, priority is configured as in the priority subcommand of the vpn load-balancing CLI command. - UDP packets on the outside for the Hello request/response messages are exchanged. The port number is specified in the cluster port load-balancing subcommand and is default to 9023.
As an example, if the priority is five for a load-balancing device, it attempts to send up to six ARP packets in order to see if any director device owns the cluster IP address. If a director device is detected, the ASA does not send any more ARP messages and waits 15 seconds before it sends the UDP Hello request. The director device then responds with an UDP Hello response.
Caveat for Reboot Scenarios
In a reboot situation with two ASAs in a load-balancing cluster:
- Either ASA-1 or ASA-2 was the director before the reboot.
- ASA-1 is rebooted.
- ASA-2 becomes the director if it was not the director previously.
- ASA-1 simply joins the cluster as a member after reboot.
The load-balancing algorithm might be affected by a configuration of the switch where the outside interface of the cluster devices are connected also. For example, a Spanning-Tree algorithm might cause connectivity delay when the device that is connected to the switch is rebooted.
Tip: The spanning-tree port fast command helps to speed up the process.
In some cases, a newly rebooted ASA that has load balancing enabled might attempt to become the director device (even if a director device already exists) because it cannot reach the current director device due to a connectivity delay in the switch. When there is a directorship conflict detected as a result of ARP collision, the ASA with a low Media Access Control (MAC) address wins, while the ASA with a higher MAC address gives up the director device role.
Director Reelection Process
There are two situations that cause a reelection of the director device.
Director Device Removed from the Cluster
When you disable the feature on the ASA, a broadcast message is sent to all of the cluster members in order to inform of the change, and the previously described election process is performed.
Director Device does Not Respond to Cluster Member Hello Messages
If the director device does not respond to a cluster member Hello message, it takes an ASA cluster member approximately 20 seconds to detect that the director is no longer present. The Hello messages are sent every five seconds (not configurable). If cluster members do not receive a response from the director device after four Hello messages, then the election process is triggered.
Troubleshoot
Note: Refer to the Important Information on Debug Commands Cisco article before you use debug commands.
Asa Vpn Load Balancing Site To Site Free
These debug commands can be useful with attempts to troubleshoot issues with your system:
- debug fsm 255 - Use this command in order to activate the general Finite State Machine debug. Enter the no debug all command in order to deactivate.
- debug menu vpnlb 3 - Use this command in order to activate the VPN load balancing debug trace. Enter the debug menu vpnlb 3 command once again in order to deactivate.
- debug menu vpnlb 4 - Use this command in order to activate the VPN load balancing function trace. Enter the debug menu vpnlb 4 command once again in order to deactivate.
Related Information

